Why Won't My Site Rank? Technical SEO Issues
- Brian Vastola
- May 15, 2025
- 14 min read
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Why Your Website May Struggle to Rank

If your website isn’t ranking in search results, technical SEO issues might be holding it back. These problems affect how search engines like Google interact with your site. When technical SEO issues occur, they can block Google from understanding, crawling, or indexing your pages effectively. Below, we will explain key technical SEO problems and how they impact your website’s ranking potential.
Not Indexed by Google
If Google doesn’t index your site, it won’t appear in search results. Indexing involves Google storing your site’s content in its database, making it accessible to users searching for relevant terms. Common reasons for non-indexing include “noindex” tags (which is a lay down easy fix), which tell Google not to add certain pages to the index, and robots.txt files that block Googlebot from accessing parts of your site (which is a novice dev move).
How it affects your ranking: If your site isn’t indexed, it becomes invisible to search engines. Even if your content is excellent, users won’t see it because Google doesn’t know it exists.
Reasons for non-indexing can vary, but a common cause is improper use of the "noindex" tag or blocking critical pages with robots.txt. This can happen unintentionally due to incorrect website settings or coding errors. It's important to regularly check and update these settings to ensure your site's content is being properly indexed.
Additionally, having your site indexed allows Google to gather information about your site and its relevance to certain keywords, which can impact your ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). This means that by not having your site indexed, you are missing out on potential traffic and visibility for your website.
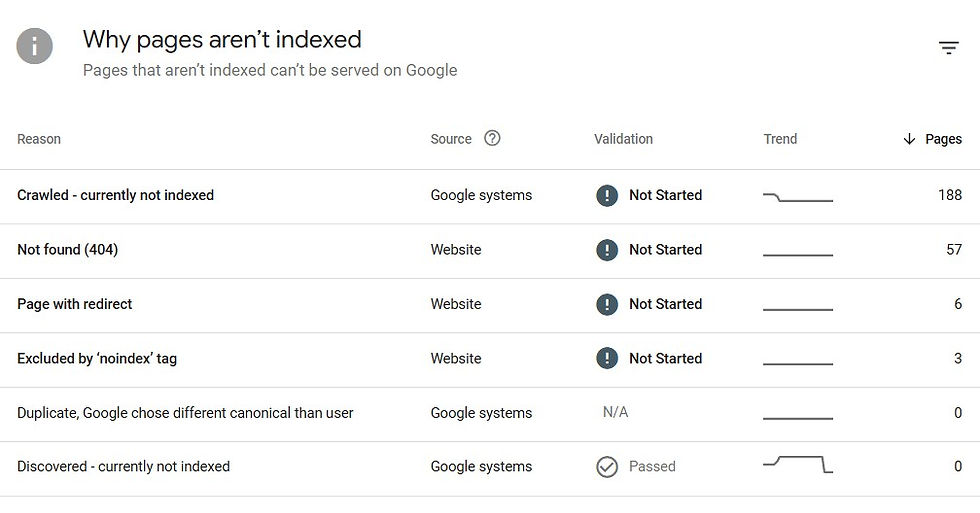
Here are some tips to help you ensure your site is being properly indexed by search engines:
Submit a sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website and their relationship to each other. By submitting a sitemap to search engines, you are providing them with a clear map of your website's structure, making it easier for them to crawl and index your site.
Use robots.txt: A robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages or sections of your website should not be crawled or indexed. This can be useful if there are certain pages on your site that you do not want to appear in search results.
However, keep in mind that this is just a suggestion for crawlers and some may still choose to ignore it.
PROTIP: To check if your WordPress site is being indexed, go to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Settings > Reading. Look for the "Search Engine Visibility" section. If the option "Discourage search engines from indexing this site" is unchecked, your site is visible to search engines. However, if it’s checked, your site is not being indexed. To enable indexing, simply uncheck this option.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
Go to Settings > Reading.
Locate the "Search Engine Visibility" section.
Ensure "Discourage search engines from indexing this site" is not checked.
Save the changes.
Poor Crawlability

Crawlability refers to how easily search engines, like Google, can browse through your website and discover its pages. When search engines "crawl" your site, they use bots—such as Googlebot—to follow links and systematically navigate your content. Think of it as creating a virtual map of your website. If your site is well-structured and easy to navigate, the bot can efficiently index your pages and understand your content. However, issues like broken links, confusing internal linking, redirect loops, or overly complex site architecture can disrupt this process, leading to poor crawlability.
How Search Engines Crawl Your Site

Search engines rely on your site's internal links to find and organize your content. For example:
Links: Googlebot follows links on your website to discover new pages. If a page isn’t linked to or is buried deep in your site, it becomes harder for Google to find.
Sitemaps: XML sitemaps act as a guide for Google, listing all the pages you want search engines to index.
Robots.txt Files: This file tells search engines which parts of your site they can or cannot crawl.

When these elements are missing, misconfigured, or flawed, your site becomes harder for search engines to crawl and index effectively.
Why Crawlability Issues Happen
Several factors can cause crawlability issues, making it difficult for Google and other search engines to navigate your site:
Broken Links: These occur when a URL is no longer valid, often showing a "404 error." Broken links prevent bots from reaching your site's content and disrupt the user experience.
Poor Internal Linking Structure: If there’s no logical flow between your pages or your most important pages aren’t linked properly, search engines may struggle to understand your site's hierarchy.
Redirect Loops: When pages redirect to each other in a loop, bots get stuck and can’t proceed to other parts of your site.
Complex Site Architecture: Overly complicated navigation or deeply buried pages make it harder for search engines to access all your content. Ideally, every page should be reachable with just a few clicks from the homepage.
Blocked Pages: Misconfigured robots.txt files or meta tags can accidentally block search engines from crawling important parts of your site.

How Poor Crawlability Impacts Your SEO and Rankings
Crawlability issues directly affect how well your site performs in search engine rankings. When search engines can’t access or understand your content, they won’t rank it effectively—or at all. Here’s how crawlability problems can hurt your site:
Missed Content: If Google can’t find all your pages due to broken links or poor internal linking, it may skip valuable content that would otherwise rank for relevant searches.
Wasted Crawl Budget: Search engines have a "crawl budget," which is the number of pages they’ll crawl on your site during a given session. If bots waste time on redirect loops or duplicate pages, they may not reach your most important content.
Lower Rankings: Even if your site contains high-quality content, crawlability issues make it harder for search engines to evaluate and rank your pages. A site that’s difficult to crawl is often deemed unreliable or poorly maintained.
Poor User Experience: Crawlability issues like broken links or confusing navigation also frustrate users, which can increase bounce rates—a signal to Google that your site might not be providing value.
How to Identify Crawlability Problems
To ensure your site is fully crawlable, you’ll need to regularly audit and optimize it. Here are some tools and strategies to identify crawlability issues:

Google Search Console: This free tool highlights crawl errors, such as broken links or blocked resources, and provides insights into how Google sees your site.
SEO Crawlers: Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can simulate how search engines crawl your site, flagging issues like broken links, redirect chains, or missing sitemaps.
Manual Checks: Navigate through your site like a user would. Test links, check navigation menus, and ensure all key pages are easily accessible.
How to Improve Crawlability
Once you’ve identified issues, take these steps to make your site more crawlable:
Fix Broken Links: Use tools to locate 404 errors and either update the links, redirect them to relevant pages, or remove them.
Simplify Site Architecture: Ensure that every page is reachable within 3 to 4 clicks from the homepage. Use a clear and logical hierarchy for your URLs.
Optimize Internal Linking: Link your pages meaningfully to guide both users and search engines through your site. Include links to high-priority pages in your navigation menu or within related content.
Create and Submit a Sitemap: Generate an XML sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console. This helps search engines find and index all your pages.
Check Robots.txt and Meta Tags: Ensure your robots.txt file isn’t blocking important pages. Avoid using "noindex" meta tags on pages you want search engines to rank.
Reduce Redirect Loops: Audit your site for redirect chains or loops and fix them to keep bots from getting stuck.
Crawlability is a foundational aspect of SEO. Without it, even the best content won’t rank because search engines can’t access or understand it. By addressing issues like broken links, poor internal linking, and overly complex site architecture, you can create a site that’s easy for both users and search engines to navigate. Regular audits and proactive fixes will ensure your site remains fully crawlable, helping you achieve better rankings and a stronger online presence.

Slow Page Speed
Page speed refers to how quickly your website loads and displays its content to visitors. It’s not just a technical metric—it plays a crucial role in user experience, search engine optimization (SEO), and overall website performance. In recent years, page speed has gained significant importance as Google has explicitly stated that it uses page speed as a ranking signal in its algorithms. A fast website creates a positive experience for users, while a slow-loading site can lead to frustration, high bounce rates, and lost opportunities. Let’s dive deeper into the nuances of page speed, why it matters, and how it can affect your website’s rankings and user engagement.
The Importance of Page Speed for Users
When someone visits your website, they expect it to load quickly and seamlessly. Research shows that most users expect a website to load in 2-3 seconds. If your site takes longer, the chances of them abandoning it increase dramatically. This is particularly true for mobile users, who often access websites on slower connections. Slow-loading pages can lead to a poor user experience, causing visitors to leave your site before engaging with its content.
From an engagement perspective, slow-loading websites can negatively impact key metrics like session duration and pages per visit. Users are far more likely to explore your website and interact with your content if pages load quickly. On the other hand, delays create friction in the user journey, increasing frustration and reducing the likelihood of conversions, such as completing a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.

How Page Speed Affects Your SEO
Google has made it clear that page speed is a ranking factor, especially in mobile search results. The company introduced the "Speed Update" in 2018, which prioritized faster-loading websites in search rankings. While Google doesn’t penalize slow websites outright, it does reward faster ones by giving them a competitive edge in search engine results pages (SERPs).
A slow-loading website can lead to higher bounce rates, which is a critical signal to Google. Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing just one page without interacting further. A high bounce rate indicates to Google that users aren’t finding value on your site, which could lower your rankings over time. Since Google’s ultimate goal is to provide users with the best possible experience, it favors websites that are not only fast but also engaging and useful.
Page speed is closely tied to other ranking factors, such as mobile-friendliness and Core Web Vitals—metrics introduced by Google to measure a site’s overall performance. These include:

Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the largest visible element (like an image or block of text) to load. A good LCP score is under 2.5 seconds.
First Input Delay (FID): Tracks the time it takes for your website to respond to a user’s first interaction, such as clicking a button or link. A faster response time enhances the user experience.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability by assessing how much elements shift unexpectedly during loading. For example, buttons or images that move around as the page loads can frustrate users.
These Core Web Vitals are now considered critical ranking factors, making page speed optimization even more essential for SEO success.
The Impact of Page Speed on Business Metrics
Beyond SEO, page speed has a direct impact on your business goals. Conversions, revenue, and customer satisfaction are all influenced by how fast your website loads. Studies have shown that even a one-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by up to 7%. For e-commerce websites, this can translate into significant revenue losses.
For example WebsiteBuilderExpert Calculates, if an online store generates $100,000 in sales per day, a one-second delay could cost $2.5 million in lost sales annually. Slow-loading pages can also damage your brand reputation, as users may associate poor performance with a lack of professionalism or reliability.
Another great example is Amazon, Amazon calculated that a page load slowdown of just one second could cost it $1.6 billion in sales each year.
Factors That Affect Page Speed
Several factors influence how quickly a website loads, including:
Server Performance: The speed and reliability of your web hosting provider play a crucial role. A slow server can delay the delivery of content to users.
Image Optimization: Large, uncompressed images are one of the most common reasons for slow-loading websites. Optimizing images by reducing their file size without sacrificing quality can significantly improve page speed.
Code Efficiency: Bloated or poorly written code, including JavaScript and CSS, can slow down your website. Minifying your code (removing unnecessary spaces and characters) and eliminating unused scripts can help.
Caching: Effective caching stores a version of your website locally on a user’s device, so they don’t have to reload the entire site every time they visit.
Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN distributes your website’s content across multiple servers worldwide, allowing users to access it from a server closer to their location.
Third-Party Scripts: External elements like ads, social media plugins, or tracking codes can add significant load time to your site. It’s important to keep these scripts to a minimum and ensure they load asynchronously.
Optimizing Page Speed
Improving page speed involves addressing the factors mentioned above. Here are some actionable steps to take:
Use a reliable web hosting provider: Invest in a high-performance server or consider upgrading to a dedicated or cloud-based hosting solution.
Optimize images: Use modern file formats like WebP and compress images to reduce file size. Tools like TinyPNG or built-in CMS features can help.
Leverage browser caching: Enable caching so repeat visitors can load your site faster.
Minify code: Remove unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Enable lazy loading: Load images and other non-critical elements only when they are visible to the user.
Reduce redirects: Minimize the number of redirects on your site, as each one adds additional load time.
Audit third-party scripts: Regularly review and remove unnecessary third-party scripts to reduce their impact on performance.
Page speed is more than just a technical metric—it’s a fundamental aspect of user experience, SEO performance, and business success. A slow website can lead to frustrated users, lower search rankings, and missed opportunities, while a fast-loading site can improve engagement, conversions, and customer satisfaction. By understanding the nuances of page speed and taking steps to optimize it, you can create a website that not only ranks well on Google but also delights your visitors and drives meaningful results for your business.
Not Mobile-Friendly

Having a mobile-friendly website is no longer optional—it’s a must. Mobile-friendly websites are specifically designed to adapt to smaller screens like smartphones and tablets. This ensures that the layout, text, images, and navigation adjust seamlessly, making it easy for users to browse and interact with your site on any device. With mobile usage now surpassing desktop for web traffic, a mobile-friendly site is essential to meet user expectations and stay competitive.
Google’s Mobile-First Indexing
Google has shifted to "mobile-first indexing," which means it evaluates and ranks the mobile version of your website first when determining your position in search results. If your mobile site is poorly designed or missing key content from the desktop version, your search rankings can suffer—even for desktop searches. This policy highlights how critical mobile optimization is for visibility online.
How Mobile-Friendliness Impacts Rankings
Google prioritizes mobile-optimized websites in its rankings. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you risk being ranked lower, especially for mobile searches—which now make up the majority of search queries worldwide. A poor mobile experience can lead to:
Hard-to-read text
Non-clickable links
Slow loading times
Excessive zooming or scrolling
These issues frustrate users, causing them to leave your site quickly, leading to higher bounce rates and lower engagement. Google sees these signals as indicators of a low-quality site, further impacting your rankings.
Enhancing the Mobile Experience
Mobile-friendliness isn’t just about adapting layouts. It’s also about enhancing usability. Key features of a mobile-friendly site include:
Touch-friendly buttons
Simple navigation
Readable font sizes
Avoiding intrusive pop-ups
Google penalizes sites with intrusive pop-ups that disrupt the user experience, so it’s crucial to follow these guidelines to maintain your rankings.
User Satisfaction and Branding
A mobile-friendly website isn’t just about SEO—it’s about providing a great user experience. A poor mobile experience can drive users away and harm your brand’s reputation, while a smooth and responsive site builds trust and encourages repeat visits. Neglecting mobile optimization can lead to lost customers, especially as competitors prioritize seamless mobile experiences.
Optimizing your website for mobile devices is essential for SEO, user satisfaction, and staying competitive. With Google’s mobile-first indexing now the standard, businesses of all sizes must prioritize mobile performance. By focusing on responsive design, improving page speed, and meeting user expectations for accessibility, you can boost your rankings, engage users, and drive lasting success for your website.
Technical Errors
Technical errors on your website, such as 404 pages (when a page cannot be found), server errors, and incorrect URL structures, can significantly hinder your site’s accessibility to both users and search engines. These issues disrupt the flow of information and make it harder for search engines to crawl and index your site properly, which is a critical factor in determining visibility in search results. For instance, a 404 error can occur when a page is deleted or when a URL is mistyped, leaving both users and search engines unable to access the intended content. Server errors indicate problems with your hosting or server configuration, which can make your site appear unreliable to search engines. Mismanaged URL structures not only confuse users but also make it more difficult for search engine crawlers to understand the hierarchy of your site’s content.

Another important factor to consider is website security. Failing to use HTTPS, which encrypts and secures data transferred between the user and your site, can harm your search rankings. Google has been prioritizing secure connections for years, as HTTPS protects sensitive user data, builds trust, and enhances user experience. A website without HTTPS is flagged as "not secure" by modern browsers, which can deter users and signal to Google that your site is not up to standard.
How do these technical errors affect your rankings? When Google encounters issues like inaccessible pages, broken links, or missing security protocols, it may skip over your site’s content during indexing or reduce the level of trust assigned to your domain. Trust and accessibility are two key factors that influence your search rankings. If your site seems unreliable or difficult to navigate, Google is less likely to show it prominently in search results. This means fewer impressions, less traffic, and ultimately fewer opportunities to reach your audience. By addressing these issues, you can improve your site’s accessibility, enhance user trust, and increase your visibility in search engine rankings.
Problems with Sitemap

An XML sitemap is an essential tool for helping search engines like Google navigate and understand your website. Think of it as a digital roadmap that lists all the important pages on your site, showing search engines where your content lives and how it’s structured. This makes it easier for Google to crawl your site and ensure that your content is indexed properly, which is crucial if you want it to appear in search results.
If your sitemap is outdated, incomplete, or missing, it’s like handing Google an incomplete map—it becomes much harder for search engines to discover all the pages on your website. This means some of your valuable content could go unnoticed, remaining unindexed and invisible to users searching for it online.
How does this impact your site's ranking? Well, if Google can’t find certain pages on your website because they aren’t included in the sitemap, those pages won’t appear in search results. This reduces your visibility and lowers your chances of ranking for keywords related to that content. In short, without a functional XML sitemap, you're essentially making it harder for your site to compete in search results. By creating and maintaining an up-to-date sitemap, you help search engines do their job more efficiently, which can improve your site's overall performance and visibility online.

Final Thoughts on Not ranking because of Technical SEO
Technical SEO issues can create significant barriers between your website and search engines, making it harder for your pages to be indexed and ranked. These problems often prevent Google and other search engines from properly understanding your site’s structure, content, and relevance, which in turn limits your ability to reach users searching for what you offer. Issues like broken links, slow loading times, poor mobile usability, or improper indexing can have a major impact on your site’s performance. Addressing these challenges is critical for improving your rankings, increasing visibility, and ensuring a better user experience. Recognizing and resolving these technical issues is the first and most important step in optimizing your website for long-term search success. With a solid technical foundation, your site will be better equipped to compete in search results and meet the needs of your audience.
CHECK OUT THE REST OF "WHY WONT MY WEBSITE RANK?" SERIES
---> See Part 2 - Why My Site Wont Rank: On Page SEO
---> See Part 3 - Why My Site Wont Rank: Off Page SEO
---> See Part 4 - Why My Site Wont Rank: User Experience

Comments